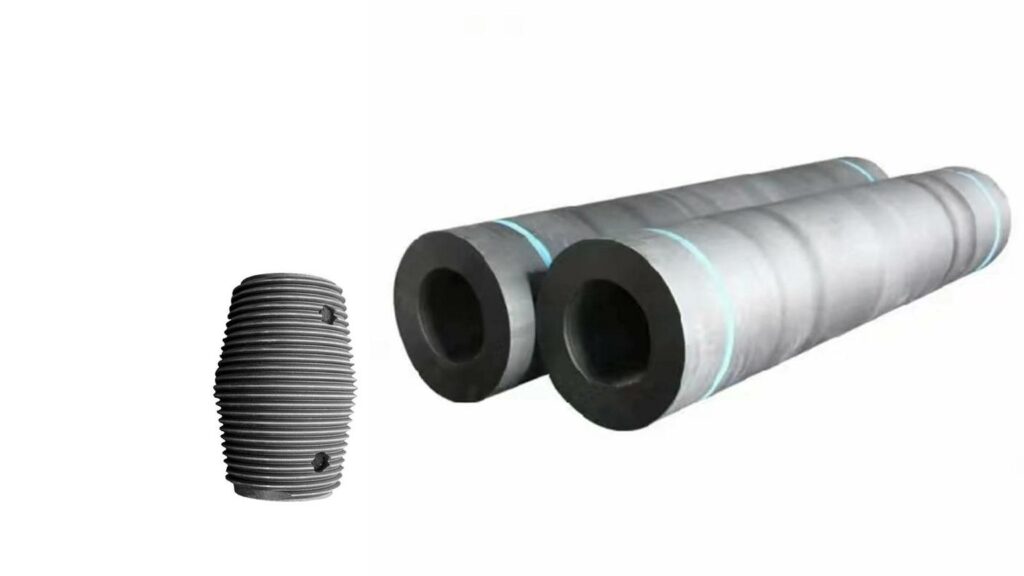
Graphite electrodes are critical to operating Electric Arc Furnaces (EAF). They conduct the high-voltage electrical current needed to heat and melt the raw materials inside, which can then be used for smelting or refining operations.
Table of Contents
ToggleTherefore, graphite electrodes are integral to producing iron, steel and other metals in the electric arc furnace. When the graphite electrodes are energized, an electric arc is created between them, heating the furnace shell and melting any metal or alloy placed within electric arc furnace.
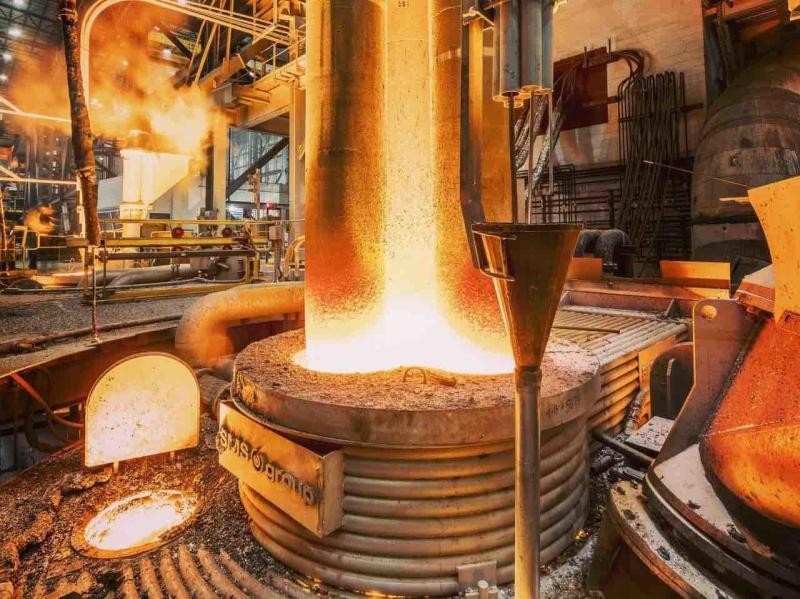
Graphite electrode melting steel process in an electric arc furnace
When an EAF is used to melt steel, the process begins with a piece of scrap metal being placed in the furnace.
Workers then connect the graphite electrodes to an external power source that provides alternating (AC) or direct (DC).
The operator then turns on the power and adjusts the current until arcs form between the graphite tips of the electrodes and the scrap metal, creating an intense heat that melts the metal into a molten liquid.
Workers pass as much as 150,000 amperes of electricity through electrodes. They create an electric arc between the graphite electrodes and the raw materials in the furnace, which causes heat to be produced.
What are electric arc furnaces and their types?
An electric arc furnace (EAF) is a specialized furnace that uses graphite electrodes to heat and melts scrap metal to produce high-quality steel.
According to the current characteristics, people divide electric arc furnaces into AC and DC electric arc furnaces. Heroult of France invented it in 1988 after the invention of electricity.
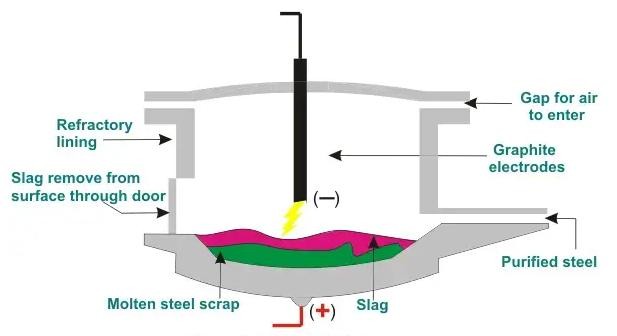
The emergence of electric arc furnaces has developed an alternative energy source for coal-based steelmaking. Electric arc furnace steelmaking enables economical recycling of scrap steel. It was ultimately making steel the most recyclable material in the world.
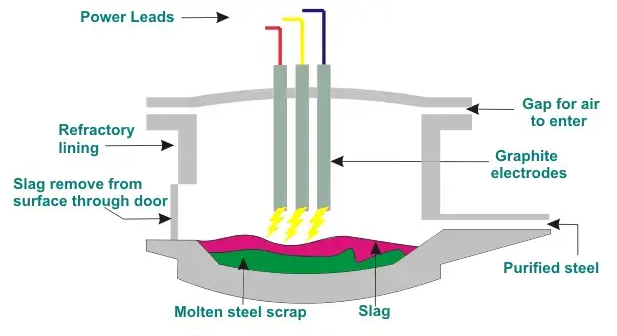
An Electric Arc Furnace work with graphite electrodes
Arc furnace electrodes conduct electrical energy from an external power source into the interior of the electric arc furnace, creating an intense heat. Usually, AC or DC electricity creates an electric arc between the graphite electrodes and the scrap material.
When the temperature reaches 5000 degrees Celsius, the high temperature melts the scrap metal into a liquid state.
Steelworkers then pour it out of the furnace. Typically, each furnace employs nine electrodes arranged in three columns of three electrodes each. The operator needs to adjust the current and voltage to use graphite electrodes in an AC electric arc furnace.
In addition, steel mill workers should use particular components such as cooling systems and shields.
Please ensure that the molten steel does not become too hot or contaminated during the process. This will help to ensure a successful output from the furnace.
The importance of graphite electrode in electric arc furnace
Graphite electrode has low resistivity and are excellent conductors for transferring electric current. The electrode with needle coke and good graphitization degree has better performance.
In addition, its thermal expansion coefficient is low and will not deform when the current gradient changes.
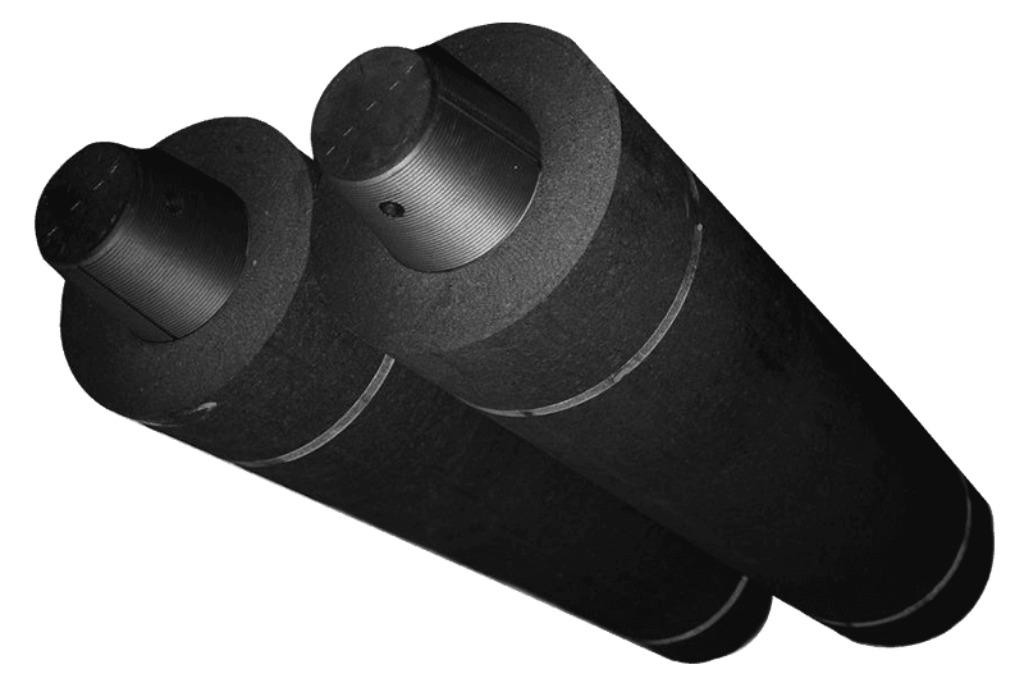

Another critical point is that it has high mechanical strength, and no bending or breaking will occur. Given these characteristics, it is well suited for high-temperature applications in electric arc furnace.
Other materials cannot be replaced, so graphite electrodes are essential in industrial production.
According to the different needs of electric arc furnace steelmaking, it has three types – RP, HP and UHP graphite electrodes.
Graphite electrodes work with Arc furnace
An Electric Arc Furnace (EAF) is a type of furnace that uses graphite electrodes to generate an electric arc to melt scrap metal. The EAF consists of a cylindrical steel shell lined with refractory materials.
The bottom of the furnace is made up of a tilting platform, which can tilt to pour out the molten metal. Workers insert graphite electrodes into the furnace through holes in the top and connect them to a power source.
When the workers turn on the power, an electric arc will generate, which heats the scrap metal and melts it. The workers pour the molten metal from the furnace and cast it into desired shapes.
The process consumes the electrodes, and workers must replace the electrodes periodically. EAFs are commonly used to recycle scrap steel and are also used in producing specialty steel.
Conclusion
Graphite electrodes are used in DC or AC electric arc furnace (eaf) to create an arc when current passes through it. Convert electrical energy into heat to smelt scrap steel or metal.
If you are looking for Graphite Electrode for Electric Arc Furnace, Reach out to us today, and let’s help you out. Please choose a professional graphite electrode manufacturer to help you with your eaf steelmaking process.
More Resources:



