In the system of elements, carbon atom has a unique and important position, which is the cornerstone of life. And it not only underpins all forms of life on Earth, but also drives innovation in materials science. Delving deeper into the structure of carbon atom can provide insight into the internal logic of the origin of life and material innovation.
Basic Information of Carbon
Atomic Number, Chemical Symbol and Atomic Mass of Carbon
The atomic number of carbon is 6 and the chemical symbol is C. Because carbon occurs in nature in the form of many isotopes, so its relative atomic mass is calculated as an average based on the relative abundance of each isotope, which is about 12.01.
Isotopes of Carbon
In nature, carbon comes in three main isotopes: carbon-12, carbon-13, and carbon-14. Carbon-12 is the most common, accounting for about 98.93% of all carbon, which nucleus contains six protons and six neutrons. These make it a standard for defining atomic mass units. Carbon-13 makes up about 1.07% of the atomic nucleus and has six protons and seven neutrons. You can often use it in nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy to help scientists study molecular structure. Carbon-14 is a radioactive isotope with a nucleus consisting of six protons and eight neutrons. It has a half-life of about 5,730 years and plays a key role in archaeology. Archaeologists can be able to date artifacts by measuring how much carbon-14 decays in them.
Analysis of Carbon Atom Structure
Atomic Models and Theoretical Development
From Dalton’s solid sphere model, to Thomson’s plum pudding model, to Rutherford’s nuclear model. As well as Bohr’s electron layered orbit model and modern quantum mechanical models, human understanding of atomic structure has been deepened. These theoretical developments laid the foundation for revealing the structure of carbon atoms. And modern quantum mechanical models suggest that electrons do not move in fixed orbits, but are distributed around the nucleus in a cloud of probability.
Details of Carbon Atomic Structure
Atomic nucleus
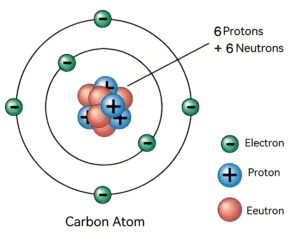
The nucleus of a carbon atom is composed of protons and neutrons, protons have a positive charge and neutrons are electrically neutral. Due to the presence of protons, the nucleus as a whole is positively charged. And because the number of positive charges is equal to the number of negative charges carried by the electrons outside the nucleus, the whole atom is electrically neutral.
Extraneous electrons
Carbon atoms have six extranuclear electrons, which are distributed in different electron layers according to their energy levels. The first layer (K layer) holds up to two electrons. The second layer (L layer) holds up to eight electrons, and the electron arrangement of carbon atoms is 2,4. That is, the K layer has two electrons and the L layer has four electrons. These four valence electrons give the carbon atom its unique chemical properties, allowing it to form stable compounds with other atoms.
Diverse Structures of Carbon
Allotropes of Carbon
Diamante
It is a hard crystal, carbon atoms through covalent bonds to build a three-dimensional tetrahedral structure, each carbon atom connects 4 adjacent atoms. This gives diamond ultra-high hardness and melting point, making it the preferred material for cutting, grinding and other industries. In addition, its bright luster also makes it a precious gem.
Grafito
It has a layered structure and the carbon atoms in the layer to form a hexagonal network of covalent bonds. The combination of weak van der Waals forces between the layers makes the graphite have good electrical conductivity and lubricity. And you can often use grafito in the manufacture of electrodes, lubricants and pencil leads.
Fullerenes and Carbon Nanotubes
Fullerenos are cage molecules composed of carbon atoms, and the most famous is C60, which is shaped like a football. Carbon nanotubes consist of carbon atoms in a tubular structure with excellent mechanical, electrical and thermal conductivity properties. You can use it to make high-performance composite materials and electronic devices.
Molecular Structures of Carbon
Molecular Structure of Carbon Dioxide
CO2 molecule consists of 1 carbon atom and 2 oxygen atoms, carbon atoms and oxygen atoms are connected by double bonds, in a straight line. This structure makes carbon dioxide gaseous at room temperature and pressure. It is an important part of the Earth’s carbon cycle and the main greenhouse gas responsible for global warming.
Organic Compounds
Organic compounds are compounds containing carbon, but do not include carbon monoxide, carbon dioxide and carbonates. The quadruvalent properties of carbon atoms enable it to form a variety of organic compounds with hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen and other atoms. They form the basis of life materials such as proteins and nucleic acids.
Special Concepts in Carbon Structures
Tertiary Carbon Atoms
Tertiary carbon atoms connect three carbon atoms and have special reactive activity in organic chemistry. In the nucleophilic substitution reaction of halogenated hydrocarbons, halogenated hydrocarbons containing tertiary carbon atoms mostly follow the SN1 mechanism. This property is different from primary and secondary halogenated hydrocarbons, which is widely used in organic synthesis.
Atomic Structure of Carbon Fibers
Fibra de carbono is composed of graphite microcrystals, atoms are arranged along the axial axis of the fiber. So that it has high strength and low density advantages. With these properties, you can widely use it in aerospace, sports equipment manufacturing and other fields.
Discovery and Applications of Carbon
Who Discovered Carbon
Carbon is one of the first elements discovered and utilized by humans. And as early as prehistoric times, humans have been using charcoal as fuel. However, it was not until the 18th century that the French chemist Lavoisier experimentally proved that carbon was an element. And based on the Latin “carbo”, he gave it the name “carbon”, meaning charcoal.
Ten Uses of Carbon
Fuel
When burned, carbon-based fuels such as wood and coal will react with oxygen. Then it can release heat for heating, cooking and power generation.
Steel production
Appropriate amount of carbon can improve the strength and hardness of steel. By regulating the carbon content, you can product different properties of steel, and use it for construction and machinery manufacturing.
Electrodo de grafito
Electrodo de grafito has good electrical conductivity and high temperature resistance. You can use it in the conductive links of electric furnace steelmaking, electrolytic aluminum and other industries.
Pencil lead
Pencil lead is made of graphite mixed with clay, and the graphite layer structure allows it to leave marks on the paper when writing.
Activated carbon adsorption
Activated carbon has rich pores, large specific surface area, which can absorb impurities and harmful substances. And you can use it in water and air purification and other scenarios.
Diamond jewelry
Diamond is an allotrope of carbon, which has bright luster, high hardness, often made into jewelry.
Material de fibra de carbono
It has high strength, low density, used in aerospace and sports equipment manufacturing to reduce weight and improve performance.
Rubber enhancement
Adding carbon black to rubber can enhance its strength, wear resistance and aging resistance, which is mostly used in tire manufacturing.
Food preservation
Activated carbon can absorb odors and harmful gases in food packaging and extend food shelf life.
Electronic products
You can also widely use carbon in electronic products, such as graphene. It has excellent electrical properties and is expected to be used in future electronic devices.
Conclusión
Carbon atom has a unique structure, rich nature and wide application. From the basic materials of life to cutting-edge scientific and technological materials, it has been found. In-depth study of the structure of carbon atoms has promoted the development of human society and help create a better future.