재료 과학의 발전은 사회 발전을 촉진하고 새로운 유형의 재료가 계속 등장하고 있습니다. 무기 흑연 질화 붕소는 흑연과 유사하고 독특한 화학 성분으로 인해 우수한 성능과 응용 가능성이 매우 높습니다. 그리고 재료 과학의 연구 핫스팟이 되었습니다.
목차
토글
무기 흑연 이름
질화 붕소를 무기 흑연이라고 부르는 이유는 무엇인가요?
질화 붕소는 흑연과 비슷한 외관을 가지고 있으며 층이 있고 미끄러운 촉감을 가지고 있기 때문에 무기 흑연이라고 불립니다. 질화 붕소의 육각형 결정 구조도 흑연과 유사하며 열 안정성이 우수합니다. 하지만 흑연은 탄소 원소로 구성되어 있는 반면 질화붕소는 질소-붕소 화합물입니다.
무기 흑연의 구조
무기 흑연 공식
무기 흑연 - 다음과 같이 알려져 있습니다. 질화 붕소의 화학식은 BN입니다. 질화붕소에서는 붕소(B)와 질소(N)가 공유 결합을 통해 1:1 화학량론적 비율로 화학적으로 결합되어 있습니다. 붕소 원자의 외부 전자 구성은 2s²2p¹이고 질소 원자의 외부 전자 구성은 2s²2p³입니다. 질화 붕소가 형성되는 동안 붕소 원자는 3개의 원자가 전자를 제공하고 질소 원자도 3개의 전자를 제공하여 결합에 참여합니다. 이러한 전자의 상호 작용은 질화붕소의 기본 구조 단위를 구성하는 안정적인 공유 결합을 형성합니다.
결정 구조 상세 분석
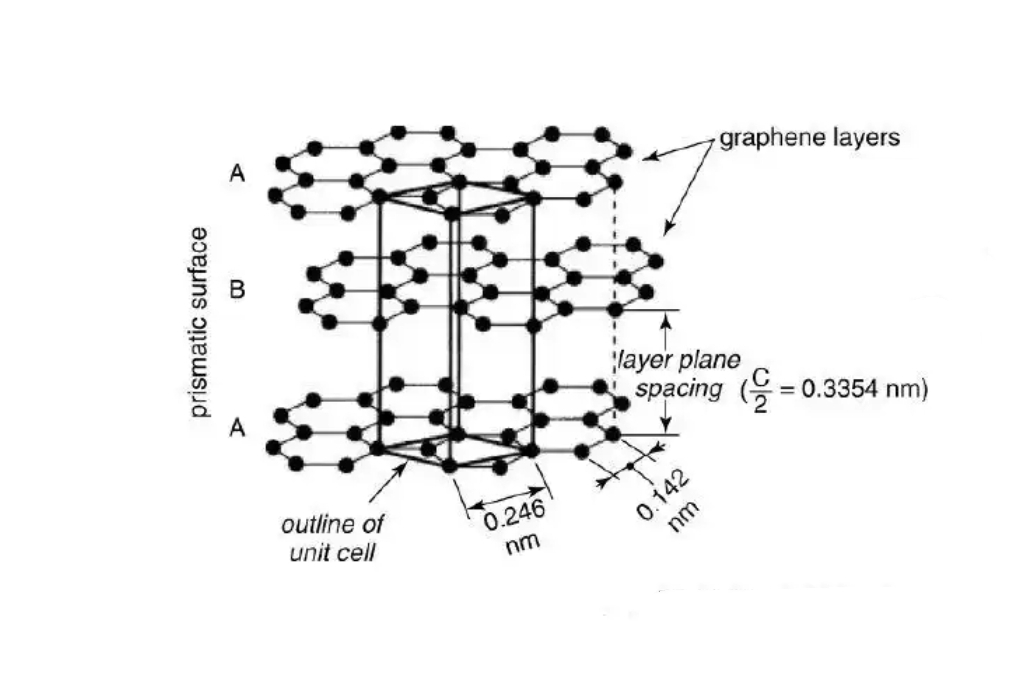
질화 붕소는 주로 육방정 질화 붕소(h-BN), 입방정 질화 붕소(c-BN), 정육면체 질화 붕소(r-BN)의 세 가지 결정 구조로 존재합니다. H-BN은 흑연과 유사한 층 구조를 가지고 있으며, 각 층은 육각형 평면 네트워크에서 붕소 원자와 질소 원자가 번갈아 가며 형성됩니다. 층들은 상대적으로 약한 반데르발스 힘을 통해 서로 상호작용합니다. 그리고 이러한 층상 구조는 육방정 질화붕소에 우수한 윤활 특성과 특정 박리성을 부여합니다. c-BN의 결정 구조는 다이아몬드와 유사하며, 붕소와 질소 원자가 사면체 형태로 연결되어 3차원 밀집 구조를 형성합니다. 이 구조 덕분에 다이아몬드 다음으로 경도가 매우 높습니다. r-BN의 구조는 육방정계 질화붕소와 입방정계 질화붕소 사이에 위치합니다. 그리고 결정 구조가 상대적으로 더 복잡하여 연구와 응용이 상대적으로 적습니다.
원자의 배열
육각형 질화붕소는 층을 이루고 있으며, 같은 층의 붕소와 질소 원자는 공유 결합으로 연결되어 있습니다. 각 붕소 원자는 세 개의 질소 원자로 둘러싸여 결합 길이가 0.145nm인 B-N 결합을 형성합니다. 이러한 결합은 평면에서 무한히 확장되는 육각형 네트워크를 형성합니다. 각 층 내의 원자들은 질서정연하게 밀접하게 배열되어 있으며, 각 층은 반데르발스 힘에 의해 서로를 붙잡고 있습니다. 층간 간격은 약 0.333nm입니다. 입방정 질화붕소에서는 붕소와 질소 원자가 공유 결합을 통해 사면체 구조를 형성합니다. 각각의 원자는 4개의 반대쪽 원자와 연결되어 단단하고 안정적입니다.
무기 흑연 하이브리드화
질화 붕소에서 육방정 질화 붕소와 입방정 질화 붕소의 붕소와 질소 원자는 주로 sp²하이브리드화됩니다. (입방정 질화 붕소는 소량의 sp³하이브리드화를 가지고 있습니다). 육방정 질화붕소를 예로 들면, 붕소와 질소 원자의 sp²하이브리드화된 궤도가 겹쳐서 σ결합을 형성하여 육각형 평면을 형성합니다. 나머지 하이브리드화되지 않은 p궤도는 평면에 수직이며 흑연의 하이브리드화와 유사하게 어깨와 어깨가 겹쳐서 비편위화된π결합을 형성합니다. 이것이 유사한 전기적 및 열적 특성의 핵심입니다.
흑연 구조의 유사점과 차이점 비교
육방정 질화 붕소와 흑연의 유사점은 둘 다 층 구조를 가지고 있으며, 층 내에는 공유 결합이, 층 사이에는 반데르발스 힘이 존재한다는 점입니다. 원자는 sp²하이브리드화를 통해 비편위π결합을 형성하고 특정 전기 전도도와 열 전도도를 갖습니다. 흑연은 층간 힘이 약해 미끄러지거나 윤활하기 쉽다는 점이 다른 점입니다. 그리고 흑연은 다음으로 구성됩니다. 탄소 원자와 질화붕소는 붕소와 질소 원자로 구성되어 있습니다. 원자 전기 음성도가 다르며 화학적 및 일부 물리적 특성도 다릅니다.
무기 흑연의 특성
물리적 속성
무기 흑연(육방정 질화 붕소를 예로 들면)은 층상 구조에서 층간 상호 작용이 약하기 때문에 윤활성이 우수합니다. 밀도는 약 2.27g/cm³이며, 항공우주 및 기타 무게가 중요한 요소인 분야에서 이점이 있습니다. 입방정 질화 붕소는 모스 경도가 9.5 - 10으로 매우 높은 경도를 가지고 있습니다. 또한 절삭 공구와 같은 내마모성 소재를 제조하는 데 사용할 수 있습니다.
화학적 특성
질화붕소는 화학적 안정성이 우수하여 상온에서 물이나 일반적인 산 및 염기와 반응하지 않습니다. 또한 고온과 강산 및 강염기에서도 비교적 안정적입니다. 고온, 강한 산화제 등이 있을 때만 천천히 산화됩니다. 따라서 화학적 환경이 열악한 산업 생산에 널리 사용될 수 있습니다.
열 속성
무기 흑연은 열 특성이 뛰어납니다. 육방정 질화붕소의 열전도율은 최대 300~400W/(m-K)로 전자 기기의 열 방출에 도움이 됩니다. 녹는점은 약 3000°C이며 고온에서도 구조와 특성이 안정적으로 유지됩니다. 따라서 항공우주 및 기타 분야의 열 보호 소재로 적합합니다.
전기적 특성
육방정 질화붕소는 밴드갭 폭이 약 6.4eV인 와이드 밴드갭 반도체 소재입니다. 반도체 분야에서 독특한 전망을 가지고 있습니다. 층 사이의 큰 π 결합이 분산되어 있기 때문에 일정한 전도성을 갖지만 금속보다 약합니다.
무기 흑연의 제조 방법
고온 고압 합성 방법
이 방법은 1000~2000℃의 고온과 5~10GPa의 고압 조건에서 작동합니다. 붕소 분말, 붕산염 및 기타 붕소 공급원, 암모니아 및 질소 가스 등이 원료로 사용됩니다. 붕소와 질소 원자의 반응을 촉진하여 질화 붕소 결정을 형성합니다. 이 방법은 결정성과 순도가 높은 정육면체 및 육각형 질화 붕소를 생산하여 고급 절삭 공구 생산에 적합합니다. 그러나 장비가 비싸고 에너지 소비가 많으며 생산량이 낮습니다.
화학 기상 증착
보란 및 기타 기체 붕소 공급원, 암모니아 및 기타 질소 공급원 등을 사용합니다. 고온과 촉매의 공동 작용으로 반응 챔버로 운반합니다. 기판 표면에서 반응하여 질화 붕소 필름을 형성합니다. 필름의 두께와 품질을 정밀하게 제어할 수 있으며 반도체 소자 제조에 자주 사용됩니다. 질화붕소 기반 전계 효과 트랜지스터 절연 층의 제조와 같은 경우입니다. 그러나 장비가 복잡하고 비용이 높으며 성장 속도가 느리다는 단점이 있습니다.
솔-젤 방식
이 방법은 순한 준비 방법입니다. 먼저 붕산염 에스테르 및 기타 붕소 공급원, 유기 아민 및 기타 질소 공급원을 유기 용매에 용해하여 균일한 용액을 형성합니다. 가수분해 및 응축 후 졸이 형성됩니다. 그런 다음 숙성되고 건조되어 겔로 변형됩니다. 마지막으로 고온 열처리를 거쳐 유기 성분을 분해하고 질화붕소를 생성합니다. 이 방법은 작동이 간단하고 비용이 저렴하며 대규모 생산이 용이합니다. 고순도 질화붕소 분말을 생산할 수 있지만 결정성이 좋지 않아 최적화가 필요합니다.
무기 흑연의 응용 분야
전자 분야
S반도체
와이드 밴드갭 반도체입니다. 질화붕소 기반 전계효과 트랜지스터의 고온 성능은 기존 실리콘 기반 제품보다 우수합니다. 질화붕소로 제작된 LED는 단파장 빛을 방출할 수 있어 자외선 통신 및 소독에 사용할 수 있습니다.
H전자 기기의 열 발산
컴퓨터 칩, 휴대폰 프로세서 및 기타 장치에서 방열판이나 코팅으로 사용할 수 있습니다. 열을 빠르게 방출하여 성능을 개선하고 수명을 연장할 수 있습니다.
에너지 분야
B아터 전극 재료
이론적으로 높은 비 용량과 안정적인 사이클링 성능을 가지고 있으며 리튬 이온, 나트륨 이온 배터리 등에 사용하기 위해 연구되고 있습니다. 그리고 전극 와 함께 탄소 소재 합성물은 배터리의 충전 속도와 수명을 향상시킬 수 있습니다.
H와이드로겐 저장 물질
특수한 구조와 전자적 특성으로 인해 수소를 흡착하고 저장할 수 있습니다. 개질 처리 후 수소 저장 용량과 안정성을 향상시킬 수 있습니다.
항공우주 분야
T열 보호 재료
녹는점이 높고 열 안정성이 우수하며 열전도율이 낮습니다. 항공기가 고속으로 비행할 때 질화붕소 기반 열 보호 소재는 열이 유입되는 것을 방지하고 내부 구조와 장비를 보호할 수 있습니다.
A항공기 부품
밀도가 낮고 강도가 높습니다. 기본 복합 재료는 항공기 날개, 동체 구조 부품 등을 제조하는 데 사용됩니다. 무게를 줄이고 구조적 강도와 신뢰성을 향상시킬 수 있습니다.
기계 분야
H고온 윤활제
육방정 질화붕소의 층상 구조로 인해 윤활성과 고온 안정성이 우수합니다. 따라서 고온 생산 공정에서 윤활제로 사용하여 마찰을 줄이고 마모를 줄이며 효율성을 개선할 수 있습니다.
W귀를 보호하는 소재
입방정 질화 붕소는 경도가 높습니다. 이 소재로 만든 공구와 연삭 공구는 절삭 및 연삭 시 내마모성과 절삭 성능이 뛰어납니다. 또한 가공 정확도를 향상시키고 공구 수명을 연장할 수 있습니다.
결론
무기 흑연(질화붕소)은 독특한 구조와 우수한 성능, 다양한 제조 방법을 가지고 있습니다. 하지만 비용과 대량 생산이라는 과제를 안고 있습니다. 연구와 기술의 발전으로 더 많은 분야에서 획기적인 발전을 이룰 것으로 기대됩니다.